OpenShiftを使ってみる - 3
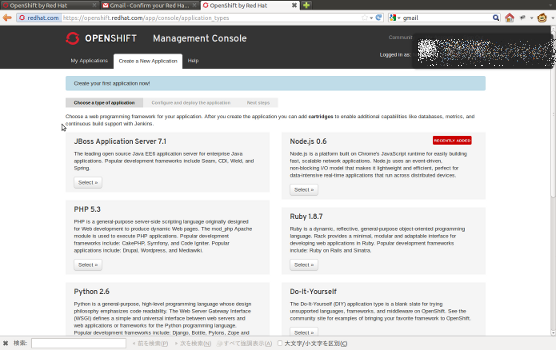
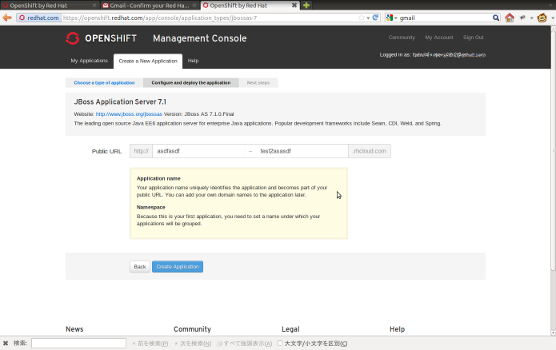
OpenShiftを使ってみる、第三弾としてOpenShiftにアプリケーションをデプロイする方法をまとめます。
JBoss ASを利用した場合の一通りの導入はまとめたと思っているので、一旦このシリーズは終了です。
方法として大きく2種類あります。開発スタイルや好みに応じて選んでください。
- ソースコードをOpenShiftにPushして、OpenShift上でビルド&デプロイ
- 予めビルドしたものをOpenShiftにPushしてデプロイ
また、どちらの方法でもOpenShiftに対してPushを行うと以下のような挙動を行います。
- JBossの停止
- .openshift/action_hooks/pre-build.sh実行
- 「openshift」プロファイルでmavenのビルド実行
- .openshift/action_hooks/build.sh実行
- .openshift/action_hooks/deploy実行
- JBossの開始
- .openshift/action_hooks/post_deploy実行
ソースコードをOpenShiftにPushして、OpenShift上でビルド&デプロイ
OpenShiftではビルドにMavenを利用します。そのため、pom.xmlが必要になりますが、OpenShiftからCloneしたリポジトリにはWARプロジェクト用のpom.xmlがあります。
WARで開発を行う場合は、このpom.xmlをもとにして開発を行うと容易にOpenShiftでのビルドとデプロイが可能です。
EARの場合、pom.xmlを別途作成する必要があります。
ポイントはEARパッケージのpom.xmlに以下のような設定を加え、deploymentsフォルダにEARファイルを出力させることです。
<profile> <id>openshift</id> <build> <finalName>ROOT</finalName> <plugins> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-ear-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.6</version> <configuration> <version>6</version> <defaultLibBundleDir>lib</defaultLibBundleDir> <outputDirectory>deployments</outputDirectory> <modules> <webModule> <groupId>groupId</groupId> <artifactId>artifactId</artifactId> <contextRoot>/</contextRoot> </webModule> <ejbModule> <groupId>groupId</groupId> <artifactId>artifactId</artifactId> </ejbModule> </modules> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </profile>
予めビルドしたものをOpenShiftにPushしてデプロイ
この方法では予めビルドしておいたアプリケーションをOpenShiftにデプロイします。
GitやMavenを利用しない開発ではこの方法が良いかもしれません。
まずは誤ってビルドが実行されないように、以下を削除します。
- pom.xml
- src
次にデプロイ対象をdeploymentsに配置します。
そしてコミットを行いPushを行うことでデプロイします。
以下はこの方法を用いた場合のリポジトリのディレクトリ構成となります。
├── .gitignore ├── .openshift │ ├── action_hooks │ │ ├── build │ │ ├── deploy │ │ ├── post_deploy │ │ └── pre_build │ ├── config │ │ ├── modules │ │ │ └── README │ │ └── standalone.xml │ ├── cron │ │ ├── README.cron │ │ ├── daily │ │ │ └── .gitignore │ │ ├── hourly │ │ │ └── .gitignore │ │ ├── minutely │ │ │ └── .gitignore │ │ ├── monthly │ │ │ └── .gitignore │ │ └── weekly │ │ ├── README │ │ ├── chrono.dat │ │ ├── chronograph │ │ ├── jobs.allow │ │ └── jobs.deny │ └── markers │ └── README ├── README └── deployments ├── .gitkeep └── ROOT.war
OpenShiftを使ってみる - 2
OpenShiftのアカウント登録からデプロイ用リポジトリのCloneまでが前回の手順ですが、今度はDBの作成を行います。
コマンドラインクライアントツールの導入(必要であれば)
公式ドキュメントを参照のこと
http://docs.redhat.com/docs/en-US/OpenShift/2.0/html-single/Getting_Started_Guide/index.html
OpenShiftClientToolをインストールする
#(その1をクリアしているならきっと入ってる…!) $ sudo apt-get install git-core # Rubyインタプリタを入れる。自力コンパイルでもRVMでも何でも良い。 $ sudo apt-get install ruby1.9.1 $ sudo apt-get install rubygems # RubyGemでOpenShiftClientToolを入れる。 # sudoは環境に応じて。 $ sudo gem install rhc
rhcコマンドのPATHが通っていなければ~/.profile or ~/.bash_profileに追記
vi .profile export PATH=/var/lib/gems/1.8/bin:$PATH
データベースを追加する(PostgreSQL8.4)
「PostgreSQL Database 8.4」を選択する。

完了画面が表示されるので、接続情報などを確認する。
また、OpenShiftクライアントコンソールでのPostgreSQLの操作方法もあるのであわせて確認する。

You can get a list of cartridges by running
rhc app cartridge list
You can manage the cartridge by running one of these commands
rhc app cartridge start -a $APP_NAME -c postgresql-8.4
rhc app cartridge stop -a $APP_NAME -c postgresql-8.4
rhc app cartridge restart -a $APP_NAME -c postgresql-8.4
rhc app cartridge reload -a $APP_NAME -c postgresql-8.4
rhc app cartridge status -a $APP_NAME -c postgresql-8.4You can remove the cartridge by running the following command.
Warning: make sure you've backed up any data you wish to keep before running this commandrhc app cartridge remove -a $APP_NAME -c postgresql-8.4
JBossのデータソース設定を確認する
OpenShiftからクローンしたデプロイ用のローカルリポジトリに移動する。
cd $LOCAL_REPO/.openshift/config vi standalone.xml
すぐに利用できる形でデータソースが設定されている。必要に応じてJNDI名を変更等する。
環境変数はOpenShift側ですでに持っているため、このままで動作する。
<datasource jndi-name="java:jboss/datasources/PostgreSQLDS" enabled="${postgresql.enabled}" use-java-context="true" pool-name="PostgreSQLDS" use-ccm="true"> <connection-url>jdbc:postgresql://${env.OPENSHIFT_DB_HOST}:${env.OPENSHIFT_DB_PORT}/${env.OPENSHIFT_GEAR_NAME}</connection-url> <driver>postgresql</driver> <security> <user-name>${env.OPENSHIFT_DB_USERNAME}</user-name> <password>${env.OPENSHIFT_DB_PASSWORD}</password> </security> </datasource>
これでDBの利用準備が完了しました。
OpenShiftを使ってみる - 1
RedHatによるPaaSサービス、「OpenShift」を始めるための手順をメモとして残します。
まずは第1段としてOpenShiftのアカウントの作成から環境の作成、リポジトリのCloneまでを行います。
事前準備
- SSH公開鍵の準備
- Gitの導入
Janetter検索ポップアップの検索エンジンを変更する
Janetterでは文字列選択時のポップアップによる検索についてはプラグインにて実現しているようです。
検索エンジンをYahooから変更したい場合、そのプラグインを書き換えてあげれば検索エンジンを変更できます。
もともと日本語圏以外はGoogleを利用する設定のようですので、日本語圏用の処理をコメントアウトするだけです。
なお、変更するかどうかは各個人で判断をお願いします。
C:\Program Files\Janetter2\Theme\Common\js\plugins\searchpopup.js
修正前
function getLink(selection) { // // Janetterの開発は皆さまのYahoo!検索によって支えられております。ありがとうございます! // if((jn.conf && jn.conf.lang ? jn.conf.lang : 'ja')=='ja'){ return 'http://search.yahoo.co.jp/search?ei=UTF-8&fr=sb-jane&p=' + encodeURIComponent(selection); }else{ return 'http://www.google.com/search?ie=UTF-8&oe=UTF-8&q=' + encodeURIComponent(selection); } }
修正後
function getLink(selection) { // // Janetterの開発は皆さまのYahoo!検索によって支えられております。ありがとうございます! // /* if((jn.conf && jn.conf.lang ? jn.conf.lang : 'ja')=='ja'){ return 'http://search.yahoo.co.jp/search?ei=UTF-8&fr=sb-jane&p=' + encodeURIComponent(selection); }else{ */ return 'http://www.google.com/search?ie=UTF-8&oe=UTF-8&q=' + encodeURIComponent(selection); //} }
Janetterの「Yahoo! 検索」をGoogleに変更する
JanetterのWeb検索エンジン変更第2弾。
右クリック時の「Yahoo!で検索」をGoogleでの検索に変更する方法です。
表示用のリソースファイルja.jsonと検索処理用のapi.jsを変更します。
1.C:\Program Files\Janetter2\bin\locale\ja.jsonを変更する
修正前
"webSearch":"Yahoo! 検索",
修正後
"webSearch":"Google 検索",
2.C:\Program Files\Janetter2\Theme\Common\js\janet\api.jsを変更する
修正前
//------------------------------------------------ // Web検索のURL取得 //------------------------------------------------ jn.webSearchUrl = function(word){ var url; word = encodeURIComponent(word); if(jn.conf.lang=='ja') url = jn.YAHOOCOJP_SEARCH_URI.format(word); else url = jn.GOOGLE_SEARCH_URI.format(word); return url; };
修正後
//------------------------------------------------ // Web検索のURL取得 //------------------------------------------------ jn.webSearchUrl = function(word){ var url; word = encodeURIComponent(word); //if(jn.conf.lang=='ja') // url = jn.YAHOOCOJP_SEARCH_URI.format(word); //else url = jn.GOOGLE_SEARCH_URI.format(word); return url; };
JSF2+CDI+Twitter4Jでカンバセーション内でOAuth認証を行う
個人的にハマりどころがあったのでJSF2+CDI+Twitter4JでのOAuth認証の方法をポイントだけまとめます。
JBoss7.1.0と7.1.1、GlassFish3.1.2で動作の確認をしています。
Twitterインスタンスを提供します。
TwitterFactoryはスレッドセーフのようなので共有し、Twitterをセッションに供給します。
@ApplicationScoped public class TwitterProducer { private TwitterFactory twitterFactory = new TwitterFactory(); @SessionScoped @Produces protected Twitter getTwitter() { return twitterFactory.getInstance(); } }
供給されたTwitterを利用してTwitterの認証系処理を行います。
状態を持つ必要はないのでステートレスにしています。
@Stateless public class TwitterOAuthService { @Inject private Twitter twitter; /** * Twitter認証用URLを取得する */ public RequestToken getRequestToken(String callbackURL) throws TwitterException { RequestToken requestToken = twitter.getOAuthRequestToken(callbackURL); return requestToken; } /** * Twitter認証のCallback処理を受け取る */ public AccessToken callback(RequestToken requestToken, String verifier) throws TwitterException { return twitter.getOAuthAccessToken(requestToken, verifier); } }
ログイン開始の処理です。
カンバセーションを開始してIDを取得するのがポイントです。
また、RequestTokenをカンバセーションにアウトジェクトしてコールバック時に備えます。
RequestTokenをカンバセーションに入れているのは、コールバックしたときに使いたいけれども、
セッションに入れても今後使わないだろうという推測からです。
Weld(CDIの実装)では現在カンバセーション開始した後のリダイレクトに問題があるようなので無理やりリダイレクトをかける必要があります。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core" xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets"> <h:form> <fieldset> <legend>ログイン</legend> <h:commandButton value="ログイン" action="#{loginAction.login()}" /> </fieldset> </h:form> </html>
@Named @ConversationScoped public class LoginAction implements Serializable { @Inject private TwitterOAuthService twitterLoginSrv; @Produces private RequestToken requestToken; @Inject private Conversation conversation; public void login() throws TwitterException, IOException { conversation.begin(); ExternalContext extCtxt = FacesContext.getCurrentInstance().getExternalContext(); String callbackURL = extCtxt.getRequestScheme() + "://" + extCtxt.getRequestServerName() + ":" + extCtxt.getRequestServerPort() + extCtxt.getRequestContextPath() + "/faces/callback.xhtml?cid=" + conversation.getId(); requestToken = twitterLoginSrv.getRequestToken(callbackURL); // カンバセーションを開始すると外部サイトのリダイレクトがおかしくなる // https://issues.jboss.org/browse/WELD-1044 // https://community.jboss.org/thread/180205 // // extCtxt.redirect(requestToken.getAuthenticationURL()); Object obj = extCtxt.getResponse(); if (obj instanceof HttpServletResponse) { HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) obj; // ExternalContext.redirectと同じ結果になる。 //response.sendRedirect(response.encodeURL(requestToken.getAuthenticationURL())); response.setHeader("Location", response.encodeRedirectURL(requestToken.getAuthenticationURL())); response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_SEE_OTHER); response.getWriter().flush(); } } }
コールバックを受け取る処理です。
ポイントはviewParamを用いてGETのパラメータを取り出し、preRenderViewで処理する点です。
また、ログイン開始と同じカンバセーションになるため、RequestTokenを取り出して使います。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core" xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets"> <h:head> <f:metadata> <f:viewParam name="#{callbackAction.oauthVerifierName}" value="#{callbackAction.oautuVerifierValue}" required="true" requiredMessage="Error"/> <f:event type="preRenderView" listener="#{callbackAction.callback()}"/> </f:metadata> </h:head> <h:body> </h:body> </html>
@Named @ConversationScoped public class CallbackAction implements Serializable { @Inject private TwitterOAuthService twitterLoginSrv; @Inject private RequestToken requestToken; private String oauthVerifierName = "oauth_verifier"; private String oautuVerifierValue; @Inject private Conversation conversation; public void callback() throws TwitterException { twitterLoginSrv.callback(requestToken, getOautuVerifierValue()); conversation.end(); } public String getOauthVerifierName() { return oauthVerifierName; } public String getOautuVerifierValue() { return oautuVerifierValue; } public void setOautuVerifierValue(String oautuVerifierValue) { this.oautuVerifierValue = oautuVerifierValue; } }
あとはbeans.xmlやtwitter4j.propertiesに注意。